- Have any questions?
- (+91) 02792 230240
- info@smcgh.edu.in

Fatigue & Exhaustion could indicate a health concern
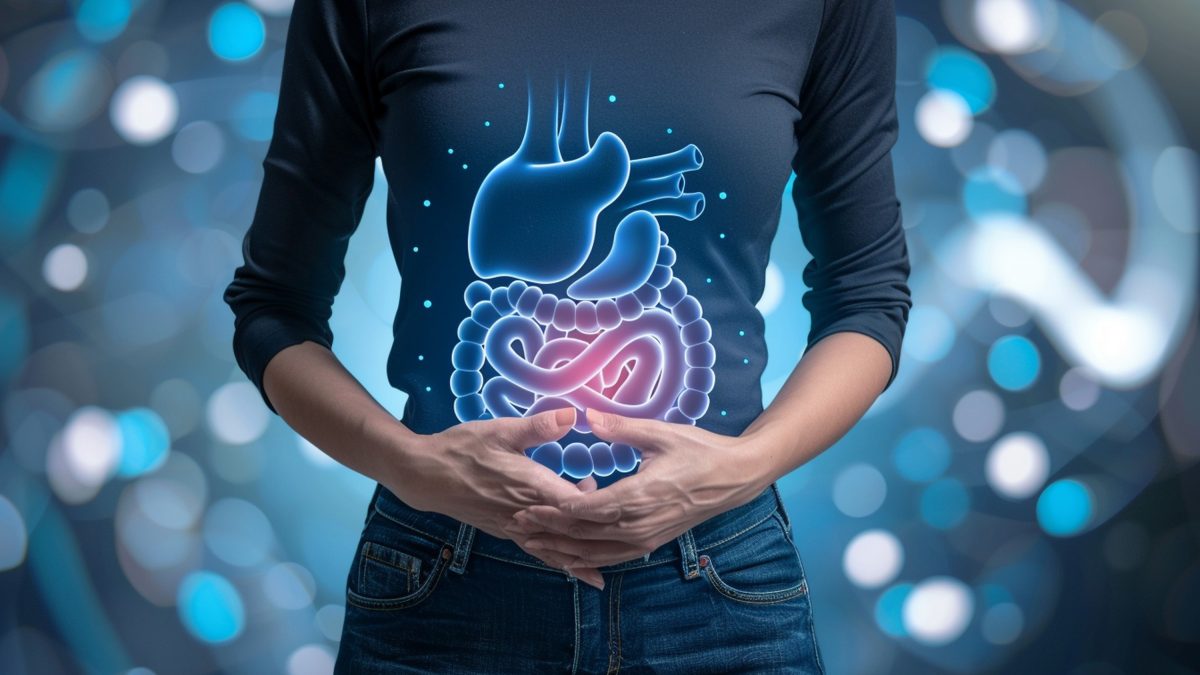
August 14, 2024The human body has a complex yet interesting way of breaking down food, ensuring it gives us the energy to function efficiently. One of the major parts involved with this process is the gut, also known as the gastrointestinal tract. It is responsible for the digestion of food, absorption of nutrients, and removal of wastes. Gut health refers to the balance and function among the many microorganisms living in the digestive tract. These microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome, significantly contribute to supporting your gut and overall health.
Importance
- Better digestion: A healthy gut ensures that food is properly digested and nutrients are absorbed efficiently. This prevents digestive discomfort and ensures your body gets the nutrients it needs.
- Immunity boost: Many parts of the immune system are located in your gut. Hence, a healthy gut can make you develop immunity to diseases, helping you fight infections and illnesses more effectively.
- Better mental health: A good healthy gut comforts the brain. The production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin emanates from the gut to aid in the modulation and regulation of mood and general mental well-being. This works against the development of mental health disorders like anxiety and depression.
- Reduces inflammation: Good gut health reduces inflammation in the body, thereby cutting the risks for chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis.
- Weight management: When the gut is healthy, it processes food efficiently and also absorbs all the nutrients from what you eat. It regulates the hormones that control appetite and thus body weight can be balanced.

Signs of an unhealthy gut
- Digestive problems: The most obvious symptom is bad digestion reflected through
bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, and heartburn. This usually is the result of an
imbalance in gut processes related to food digestion. - Unintentional weight change: Inadvertent weight gain or loss of a large amount without
changes in diet and over-exercise may be the first sign of a gut gone wrong. This will
affect nutrient absorption, blood sugar control, and how much fat your body can store. - Fatigue and sleep Irregularities: Due to an imbalanced gut, one may be chronically
fatigued and even develop sleep disorders, which may include insomnia. The gut is
responsible for a huge amount of production of the hormone serotonin, relating to mood
and sleep. - Skin conditions: Inflammation in the gut is associated with skin inflammation as well.
Hence, it may lead to skin conditions, for example, eczema and acne. - Food intolerances: If you notice sudden intolerance to some food, this could be a
symptom of an unhealthy gut. Poor gut bacteria can only digest poor foods; in this case,
some will not digest well, causing bloating, gas and stomach aches. - Autoimmune diseases: Systemic inflammation because of an unhealthy gut would in turn
lead to a change in how immune processes work and result in autoimmune diseases
where the body attacks its tissues. - Mental health disorders: The mood-regulating hormones produced by the gut have a
strong connection with the brain. An unhealthy gut can hence lead to anxiety,
depression, and mood swings.
Treatment
- Probiotics and prebiotics: Probiotics introduce good bacteria into the gut, hence
re-balancing it and improving digestion. This can reduce some symptoms of the
digestive diseases by reducing them. Prebiotics feed these good bacteria, hence
enabling them to grow and survive in the gut, promoting good digestive health. Together,
they improve gut health and treat a range of digestive problems. - Nutrition: Include a sufficient amount of food high in fiber such as fruits, vegetables,
legumes, whole grains and avoid highly processed foods, rich in refined sugars and
artificial sweeteners. - Water: Hydration is key to easy digestion, which in turn keeps the gut healthy.
- Stress reduction mechanisms: Use of stress handling mechanisms, which encompass
stress management like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing, to gut health of the body.

Prevention
- Balanced prroper diet: Eating a wide variety of whole foods to assist in supporting a
healthy gut microbiome. - Regular exercise: Physical activity results in the production of good gut bacteria and
overall fitness of the body. - Sleep: Quality sleep should last at least 7-8 hours per night, supporting the regulatory
functions of the body, including digestion. - Prevent the overuse of antibiotics: Use these only when absolutely necessary and as
prescribed by a health physician to avoid any alteration of gut microbiota. - Stay hydrated: Water eases your digestion, ensuring that your gut is healthy.
- Stress management: Incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine
to stay away from gastrointestinal problems related to stress. - Limit processed foods: Try to avoid processed foods, they are made with artificial
sweeteners and additives that greatly damage your gut health.

Takeaway
Taking care of your gut health is important for overall health. If witnessing digestive problems, sudden weight changes, or constant tiredness, don’t hesitate to see a doctor. Remember, the warning signs could be different ways for different individuals. With a personalised action plan and lifestyle changes, you can repair your gut. Taking charge of your health now can result in a higher quality of life.




